How will Google & Yahoo's New DMARC Policy affect your email security?
Many of our clients here at DataConnectivity use Google and Yahoo as their email or web browser, so we thought we’d explain what the DMARC policy is, and why it highlights the urgency of email authentication.
So, what is it?
DMARC stands for ‘Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance’ and it’s a standard email authentication method.
Google provides the following information about DMARC
DMARC helps mail administrators prevent hackers and other attackers from spoofing their organization and domain. Spoofing is a type of attack in which the From address of an email message is forged. A spoofed message appears to be from the impersonated organization or domain.
DMARC also lets you request reports from email servers that get messages from your organization or domain. These reports have information to help you identify possible authentication issues and malicious activity for messages sent from your domain.
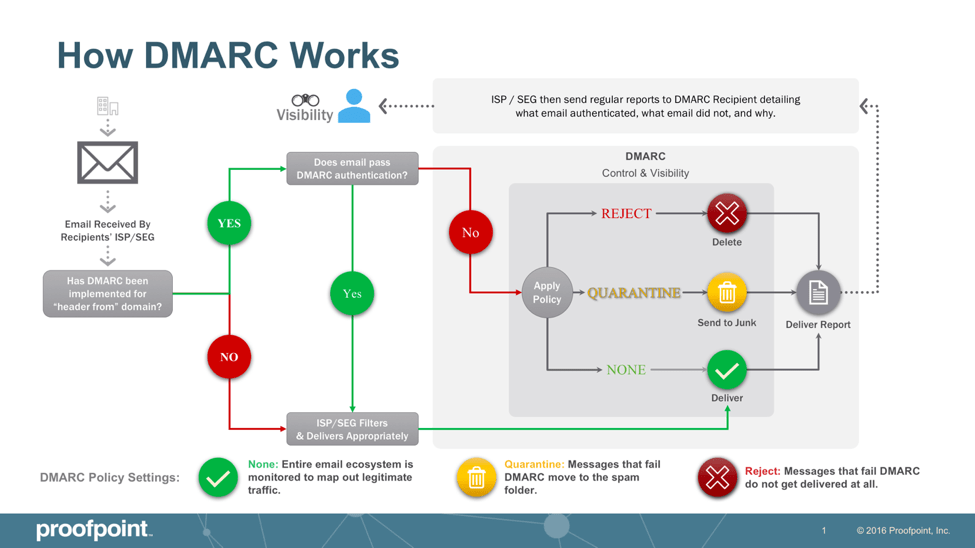
Nice summary diagram from Proofpoint
The ongoing issue of email spoofing
According to Cyberint.com, UK phishing reports indicate that 79% of organizations in the UK were targeted by phishing attacks in the past year.
We probably know of a friend or work colleague who has fallen for an email scam having clicked on a seemingly innocuous link.
The common name for this is email spoofing. It’s where scammers disguise their email addresses. They try to appear as legitimate individuals or organizations. Scammers spoof a business’s email address. Then they email customers and vendors pretending to be that business. These deceptive tactics can have devastating consequences on companies.
These include:
Financial losses
Reputational damage
Data breaches
Loss of future business
Unfortunately, email spoofing is a growing problem which makes email authentication a critical tool in a company's digital defense toolbox.
What is Email Authentication?
Microsoft 365 explains that email authentication (also known as email validation) is a group of standards to identify and prevent the delivery of email messages from forged senders (also known as spoofing). Spoofed senders are commonly used in business email compromise (BEC), phishing, and other email attacks. These standards include:
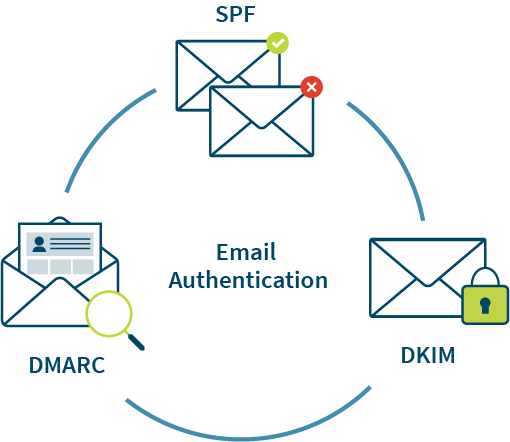
Sender Policy Framework (SPF): Specifies the source email servers that are authorized to send mail for the domain.
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM): Uses a domain to digitally sign important elements of the message to ensure the message hasn't been altered in transit.
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC): Specifies the action for messages that fail SPF or DKIM checks for senders in the domain, and specifies where to send the DMARC results (reporting).
Authenticated Received Chain (ARC): Preserves original email authentication information by known services that modify messages in transit. The destination email server can use this information to authenticate messages that would otherwise fail DMARC
SPF and DKIM are protective steps. DMARC provides information critical to security enforcement. It helps keep scammers from using your domain name in spoofing attempts.
Here's how it works:
You set up a DMARC record in your domain server settings. This record informs email receivers (like Google and Yahoo). It tells them the IP addresses authorized to send emails on your behalf.
What happens next? Your sent email arrives at the receiver’s mail server. It is looking to see if the email is from an authorized sender.
Based on your DMARC policy, the receiver can take action. This includes delivery, rejection, or quarantine.
You get reporting back from the DMARC authentication. The reports let you know if your business email is being delivered. It also tells you if scammers are spoofing your domain.
The 3 Layers of Email Authentication Protocol
Why Google & Yahoo's New DMARC Policy Matters
Both Google and Yahoo have offered some level of spam filtering. The new DMARC policy published in February 2024 raises the bar on email security.
Gmail will require email authentication to be in place when sending messages to Gmail accounts. If you're a bulk sender who sends more than 5,000 emails per day to Gmail accounts, you'll have even more email authentication requirements to meet.
Yahoo will apply the same trio of requirements to “bulk senders” in the first quarter of 2024, though they have not defined what constitutes a bulk sender.
Both companies also have policies for those sending fewer emails. These relate to SPF and DKIM authentication.
Look for email authentication requirements to continue. You need to pay attention to ensure the smooth delivery of your business email.
The Benefits of Implementing DMARC
Implementing DMARC isn't just about complying with new policies. It offers a range of benefits for your business
Protects your brand reputation: DMARC helps prevent email spoofing scams. These scams could damage your brand image and customer trust.
Improves email deliverability: Proper authentication ensures delivery. Your legitimate emails reach recipients' inboxes instead of spam folders.
Provides valuable insights: DMARC reports offer detailed information. They give visibility into how different receivers are handling your emails as well as help you identify potential issues. They also improve your email security posture.
Serving as a dedicated IT team for companies across Cambridgeshire and Suffolk, please get in touch with us if you require any assistance with your email authentication.
Featured image: Photo by Solen Feyissa on Unsplash
Shoutout to The Technology Press for their prompt on this topic.